
Don’t open email attachments from people you don’t know.You could end up playing a game you can’t win. Just because you pay a hacker doesn’t mean they have to release your data. Before you pay a ransom, explore all your options.Updates often include patches that close security holes hackers might take advantage of. Keep all other programs and applications up to date.

If you haven’t been taking steps to prevent ransomware attacks, there’s no better time to start than right now. Global ransomware damage is expected to hit $20 billion by 2021. The attacks aren’t slowing down and will likely increase in frequency and sophistication. Hackers flock to ransomware because of its potential for high payouts and minimal consequences.
#Apple ransomware attack how to#
If you’ve been lucky enough to avoid them so far, learn how to start protecting your files and data next. If you do fall victim to a ransomware attack, there are certain steps you should take immediately. That’s why it’s best to remain educated and vigilant about preventing ransomware attacks. These are just some types of ransomware and hackers are coming up with new methods all the time.
#Apple ransomware attack software#
If your device is infected, you won’t be able to access software or applications.
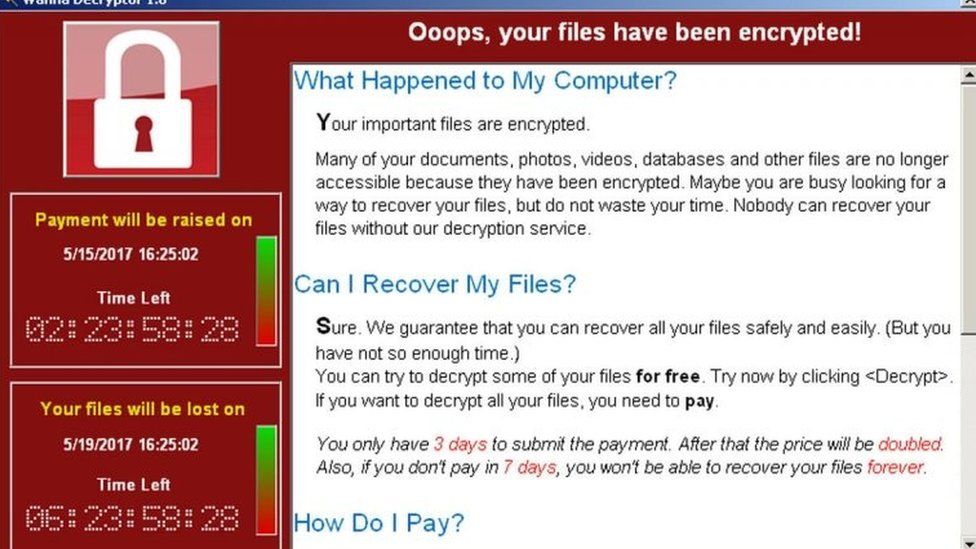
There are several things ransomware can do once it takes over a device, depending on its type. But it’s not always this black and white. What Can Ransomware Do?Īs already mentioned, ransomware typically encrypts a victim’s files and holds them hostage until a ransom payment is made. Experts expect ransomware to only become more sophisticated as hackers evolve just as quickly as technology. More aggressive forms of ransomware can exploit security vulnerabilities and attack devices without acquiring special access. This allows them to get into your files without being detected.

Most forms of ransomware include social engineering tools that trick victims into providing hackers with administrative access. Their files are now being held hostage by the attacker who is demanding a ransom payment. The email includes an attachment that they download, only to find out the attached document installed ransomware onto their computer. For example, a victim may open an email that seems to be from a trusted source. The most common is through a phishing attack. Ransomware can find its way onto your device in several ways. The hacker then demands a ransom, typically payable in cybercurrency, to restore data and files. Though there are several variations, most attacks encrypt a victim’s files. If you want to protect your files and cash, learn how to prevent ransomware attacks before it’s too late.

Unfortunately, these ransom amounts continue to grow. In 2018, the average ransomware demand was $1,077 and 10% of all ransomware demands were over $5,000.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
